Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical signals of your heart. It’s a common, non-invasive and painless test used to quickly detect heart problems and monitor the heart’s status in many situations.
During an ECG, sensors (electrodes) are attached to your chest and sometimes to your limbs to detect:
- Irregularities in your heart rhythm (arrhythmias).
- If blocked or narrowed arteries in your heart (coronary artery disease) are causing chest pain or a heart attack.
- Structural problems with your heart’s chambers.
- A previous heart attack.
- How well certain ongoing heart disease treatments, such as a pacemaker, are working.
You may need a heart rhythm test if you experience any of the following signs and symptoms:
- Heart palpitations
- Rapid pulse
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or confusion
- Weakness, fatigue or a decline in ability to exercise
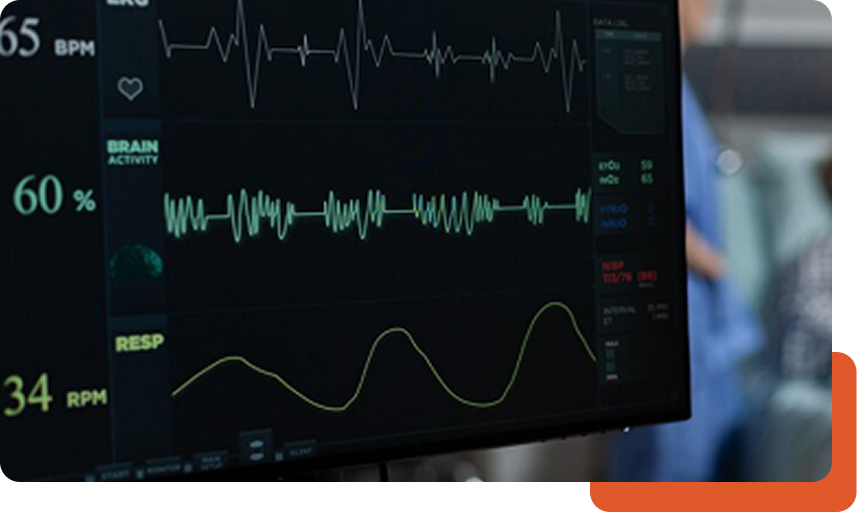
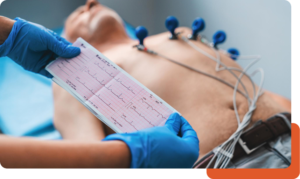 An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical signals of your heart. It’s a common, non-invasive and painless test used to quickly detect heart problems and monitor the heart’s status in many situations.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical signals of your heart. It’s a common, non-invasive and painless test used to quickly detect heart problems and monitor the heart’s status in many situations.
During an ECG, sensors (electrodes) are attached to your chest and sometimes to your limbs to detect:
- Irregularities in your heart rhythm (arrhythmias)
- If blocked or narrowed arteries in your heart (coronary artery disease) are causing chest pain or a heart attack
- Structural problems with your heart’s chambers
- A previous heart attack
- How well certain ongoing heart disease treatments, such as a pacemaker, are working
You may need a heart rhythm test if you experience any of the following signs and symptoms:
- Heart palpitations
- Rapid pulse
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or confusion
- Weakness, fatigue or a decline in ability to exercise

